Author: Sam Bullers
Contributors: Sam Bullers, Rachel Feeney, Matt Jackson
Updated: 10-07-2020
Executive Summary
The pilot study reported here aimed to determine which commercially available DNA extraction kit and homogenisation step performed the best when extracting DNA from the ZymoBIOMICS Community Standard, which is comprised of 10 microbes in known quantities.
As the ZymoBIOMICS standard is a known defined community, the best extraction kit and homogenisation method will be the protocol which results in the sequencing data closest to the initial input. The Community Standard was diluted from neat to 1:1000000 to determine if a particular extraction kit or homogenisation step yielded greater DNA concentrations and at what point DNA was no longer detected from each variable. DNA quantification was performed on a Nanodrop and all kits showed recovery of good quantity and quality DNA from both kits and both homogenisation steps. For all conditions, DNA concentration hit a base level at a 1:100 dilution.
Shotgun sequencing was performed on one replicate of the undiluted and 1:10 dilution of each extraction method and homogenisation method. From this data, we observed all conditions tested recovered all of the microbes which make up the community standard. PCA analysis showed that sample concentration (undiluted vs 1:10) or extraction kit (Qiagen vs ZymoBIOMICS) showed no significant difference in microbial DNA recovered. A significant difference in the microbial DNA composition was observed between homogenisation protocols (Tissue Lyser II vs Vortex Adapter).
Objective
To establish which commercially available DNA extraction kit and homogenisation protocol will be used by the Oxford Centre for Microbiome Studies for all future routine DNA extractions from faecal samples.
Aims
- Determine optimum DNA extraction kit between the Qiagen QIAmp PowerFecal Pro (#51804) and the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Microprep kit (#D4301) with regard to DNA yield, community standard DNA abundance recovery and general usability.
- Determine optimum homogenisation protocol between a higher-powered homogeniser (Qiagen Tissue Lyser II) and lower-powered homogeniser (Qiagen Vortex adapter) with regard to DNA yield, community standard DNA abundance recovery and usability.
- Understand at which dilution of the serially diluted community standard, the Nanodrop no longer detects DNA and if diluting the standards affects which species within the standard are detected.
Methodology
Microbial Community Standard
ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard (#D6300) was used as a defined microbial input into this series of experiments. For an extraction protocol to be successful, the sequencing output will give the same species of bacteria, in the same abundance, as the input. Any bias introduced by the extraction protocol, homogenisation protocol or dilution of the input will be detected by a bias in the sequencing output.
The theoretical composition of the ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard based on Genomic DNA: Listeria monocytogenes - 12%, Pseudomonas aeruginosa - 12%, Bacillus subtilis - 12%, Escherichia coli - 12%, Salmonella enterica - 12%, Lactobacillus fermentum - 12%, Enterococcus faecalis - 12%, Staphylococcus aureus - 12%, Saccharomyces cerevisiae - 2%, and Cryptococcus neoformans - 2%. Also see Figure 1.
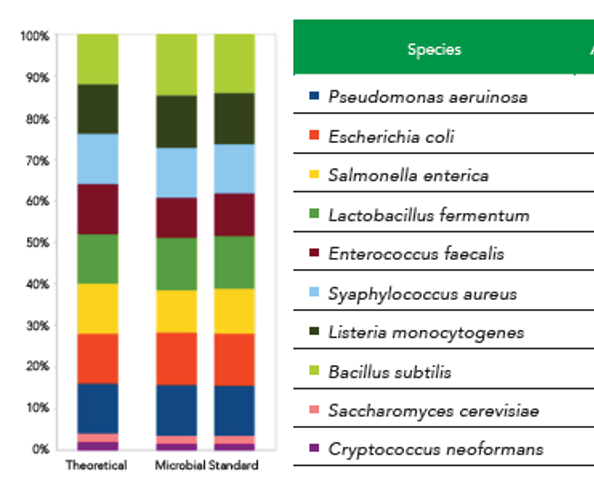
Figure 1. zymoresearch.com graphical illustration of the composition
of the ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard.
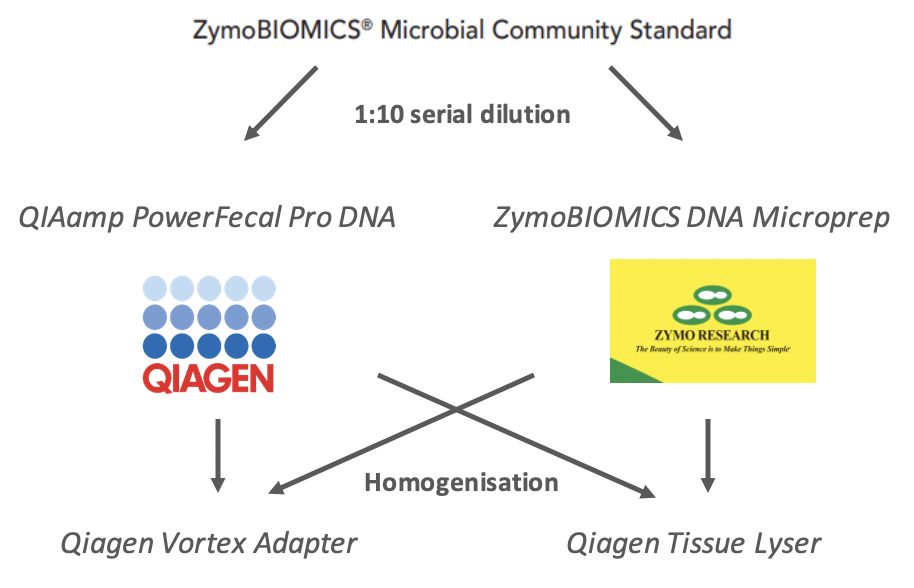
Experimental workflow
The ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard was diluted 1:10 from neat to 1:1000000 in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Diluted samples were then split into samples which would be extracted using the Qiagen QIAmp PowerFecal Pro (#51804) or the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Microprep kit (#D4301).
Samples were then further subdivided into those which were homogenised using the Qiagen Vortex Adapter for 20 minutes, as per the manufacturer’s instructions or homogenised using the Qiagen Tissue Lyser II for 2x5 minutes, with a rotation of samples in between, as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Figure 2). All sample conditions were performed in duplicate.
Extraction protocols
Half of the samples in this experiment were extracted using Qiagen QIAmp Power Fecal Pro analytical procedure with modifications to manufacturer’s instructions at the sample homogenisation step. Within this group, half the samples were homogenised with the Qiagen Vortex Adaptor on the Votex Genie, for 20 minutes. The other half were homogenised using the Tissue Lyser (5 min, turn, 5 min, at 25 Hz). After sample homogenisation, all samples were processed according to Qiagen’s instructions.
The other half of samples in this experiment were extracted using ZymoBIOMICS DNA Microprep kit analytical procedure with modifications to manufacturer’s instructions at the sample homogenisation step. Within this group, half the samples were homogenised with the Qiagen Vortex Adaptor, and the other half with the Tissue Lyser, as in the same manner as described above. After sample homogenisation, all samples were processed according to ZymoBIOMICS’s instructions.
All DNA concentrations were measure by Nanodrop before storing.
Results
Qiagen Vortex Adapter
- Homogenisation with the Qiagen Vortex Adapter resulted in good DNA yields from the undiluted ZymoBIOMICS Community Standard.
- Initial differences between kits in the undiluted standard DNA concentration was likely due the Qiagen PowerFecal kit eluting in 50uL elution buffer while the ZymoBIOMICS extraction kit recommends eluting in 20uL elution buffer.
- Qiagen PowerFecal kit showed very little variability between replicates (n=2) compared to the ZymoBIOMICS extraction kit for the undiluted sample.
- From a 1:10 dilution both kits produced a similar DNA concentration. From 1:100 dilution onward, both kits had reached a baseline just above the limit of detection for all dilutions.
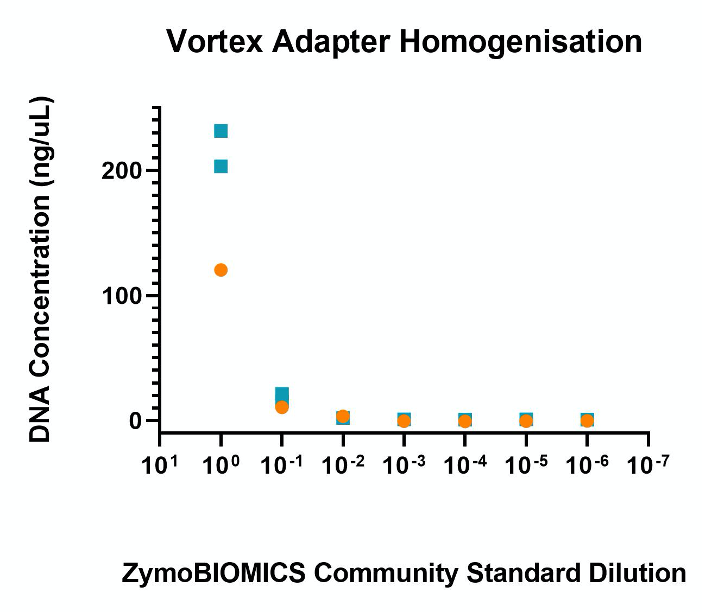
Figure 3. Nanodrop DNA quantification of DNA extracted from a serial dilution of the ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard using the Qiagen Vortex Adapter
Qiagen Tissue Lyser II
- Homogenisation with the Qiagen Vortex Adapter resulted in good DNA yields from the undiluted ZymoBIOMICS Community Standard.
- The ZymoBIOMICS extraction kit produced comparable DNA concentrations on the Tissue Lyser II to that on the Qiagen Vortex Adapter. However, the Qiagen extraction kit showed lower DNA concentration values from the undiluted standard compared to the Qiagen Vortex Adapter.
- Qiagen PowerFecal kit again showed very little variability between replicates (n=2) compared to the ZymoBIOMICS extraction kit for the undiluted sample.
- From a 1:10 dilution both kits produced a similar DNA concentration. From 1:100 dilution onward, both kits had reached a baseline just above the limit of detection for all dilutions. (Figure 4).
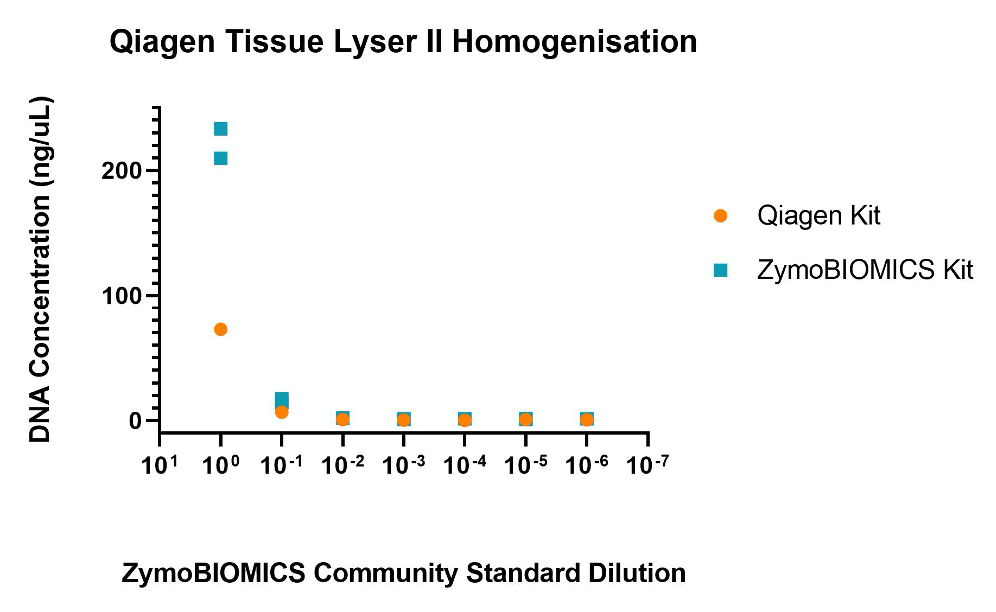
Figure 4. Nanodrop DNA quantification of DNA extracted from a serial dilution of the ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard using the Qiagen Tissue Lyser II.
Sequencing
A replicate of the undiluted and 1:10 dilution of the ZymoBIOMICS community standard from both extraction and both homogenisation methodologies was submitted for Illumina shotgun metagenomic sequencing.
Shotgun Sequencing Analysis
Analysis of the shotgun sequencing of the undiluted and 1:10 dilution of the ZymoBIOMICS community standard revealed that all microbes within the standard could be recovered in all conditions. In this analysis, sample counts are not normalised to genome size, therefore only a direct comparison to DNA input (i.e. the proportion of each microbe within the standard - DNATrue) is made.
No other microbes and little unassigned taxon indicated no contaminants were introduced during the extraction and sequencing process.
Abundance analysis showed that despite recovering all of the microbes were recovered, of the microbes that were recovered, clear differences in the abundances could be seen when compared to the true input values (Figure 5).
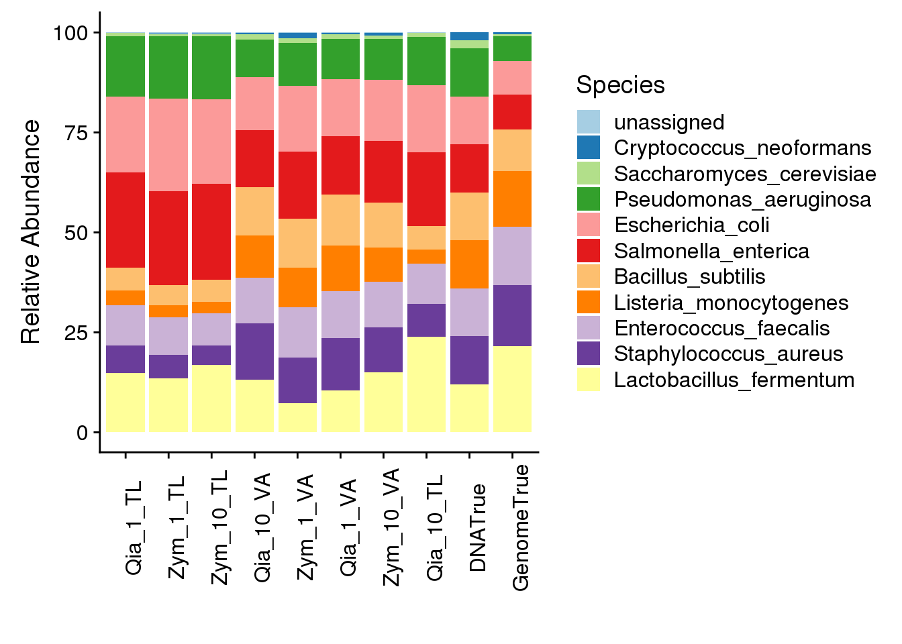
Figure 5. Abundances of the different bacterial sequences within each of the samples.
Principle component analysis allowed comparison of the different variables to determine which condition drove any differences observed and if these differences were statistically significant.
Sample Dilution
- PCA analysis showed a cluster of 4 conditions which grouped around the DNATrue value and 4 samples which separated from the DNATrue reference value (Figure 6).
- Clustering suggested that there was a group of conditions which adequately extracted the DNA from the standard to such an extent that the sequencing analysis clustered closely to the theoretical input of the community standard.
- Both of these clusters comprised of a mix of undiluted and 1:10 diluted samples indicating that diluting the neat standard 10x did not affect the sequencing output.
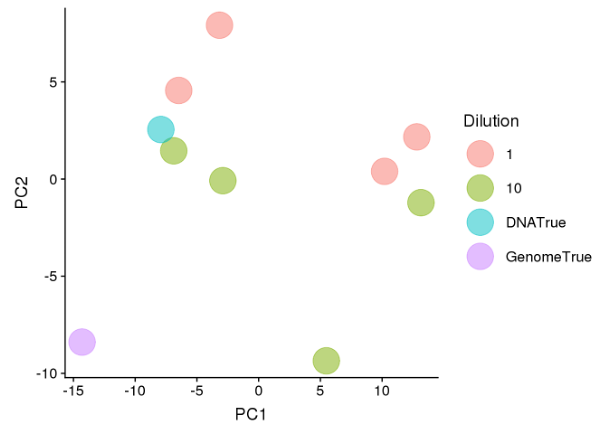
Figure 6. Principle Component Analysis of all samples for shotgun metagenomic sequencing coloured by dilution.
Extraction kit
- Both the cluster of 4 samples near the DNATrue reference value and the samples spread further from the DNATrue value comprised of a mixture of samples extracted by the Qiagen PowerFecal Pro kit and the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Microprep kit.
- The closest samples to the DNATrue reference value were extracted by the Qiagen PowerFecal Pro kit (Figure 7).
- This indicated that the sample extraction kit does not impact on the DNA extracted from the community standard and the sequencing output.
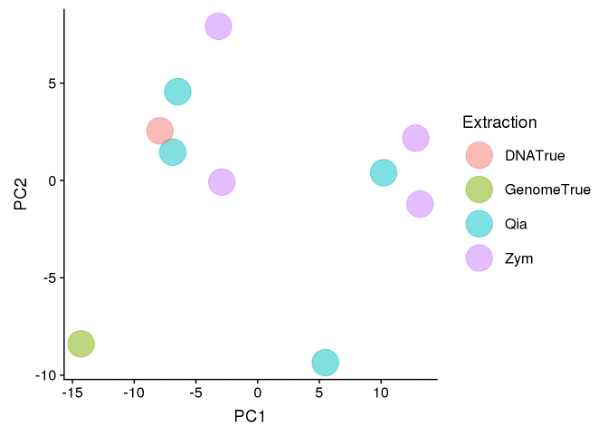
Figure 7. Principle Component Analysis of all samples for shotgun metagenomic sequencing coloured by extraction kit.
Homogeniser
- The two different homogenisation protocols; Qiagen Tissue Lyser II versus Qiagen Vortex Adapter showed a significant difference (P<0.001) in microbial sample composition (Table 1). The samples extracted by the Qiagen Vortex Adapter all clustered closely to the DNATrue reference value.
- The samples extracted by the Qiagen Tissue Lyser II clustered away from the DNATrue reference value, although still clustered together on PC1 (Figure 8 ).
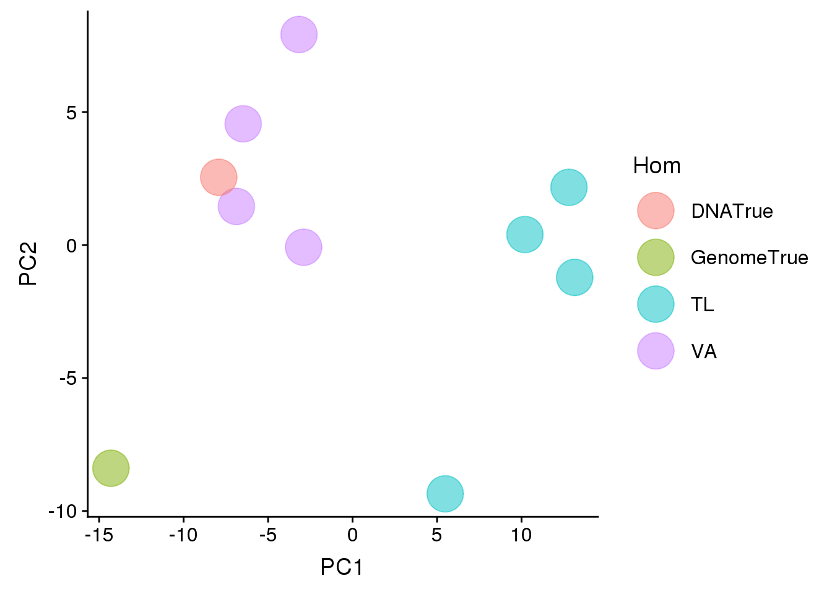
Figure 8. Principle Component Analysis of all samples for shotgun metagenomic sequencing coloured by homogeniser.
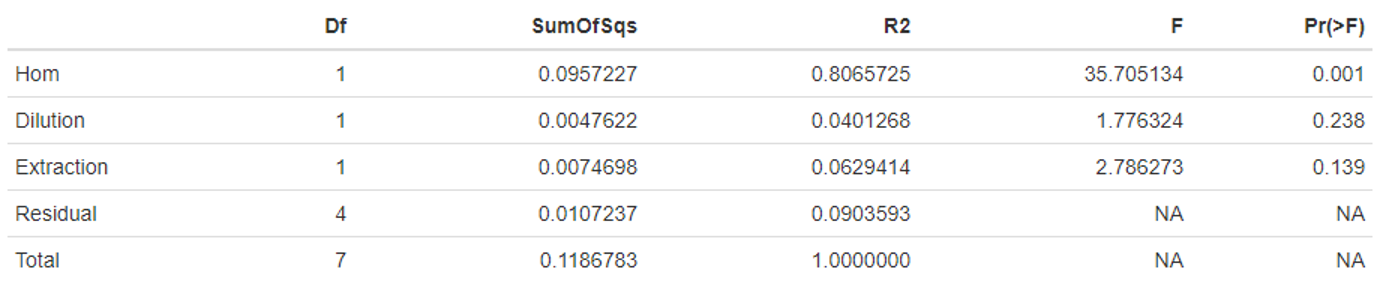 Table 1. Statistical analysis of the different variables tested
Table 1. Statistical analysis of the different variables tested
Summary
- Qiagen kit produced the most consistent DNA concentration between replicates for both homogeniser protocols, although a small n number means significance cannot be determined.
- All microbes within the ZymoBIOMICS Community Standard could be recovered in all conditions tested, although difference in abundances were observed.
- The Qiagen Tissue Lyser II showed a significant difference in the abundances of the microbial community standard sequencing results compared to the DNATrue value. Whereas the samples extracted with the Qiagen Vortex Adapter clustered closely with the DNATrue reference value.
- Extraction kit did not show a significant difference between reference value and sample value. However, samples extracted by the Qiagen PowerFecal kit cluster the closest to the DNATrue reference value when using optimal homogenisation protocol.